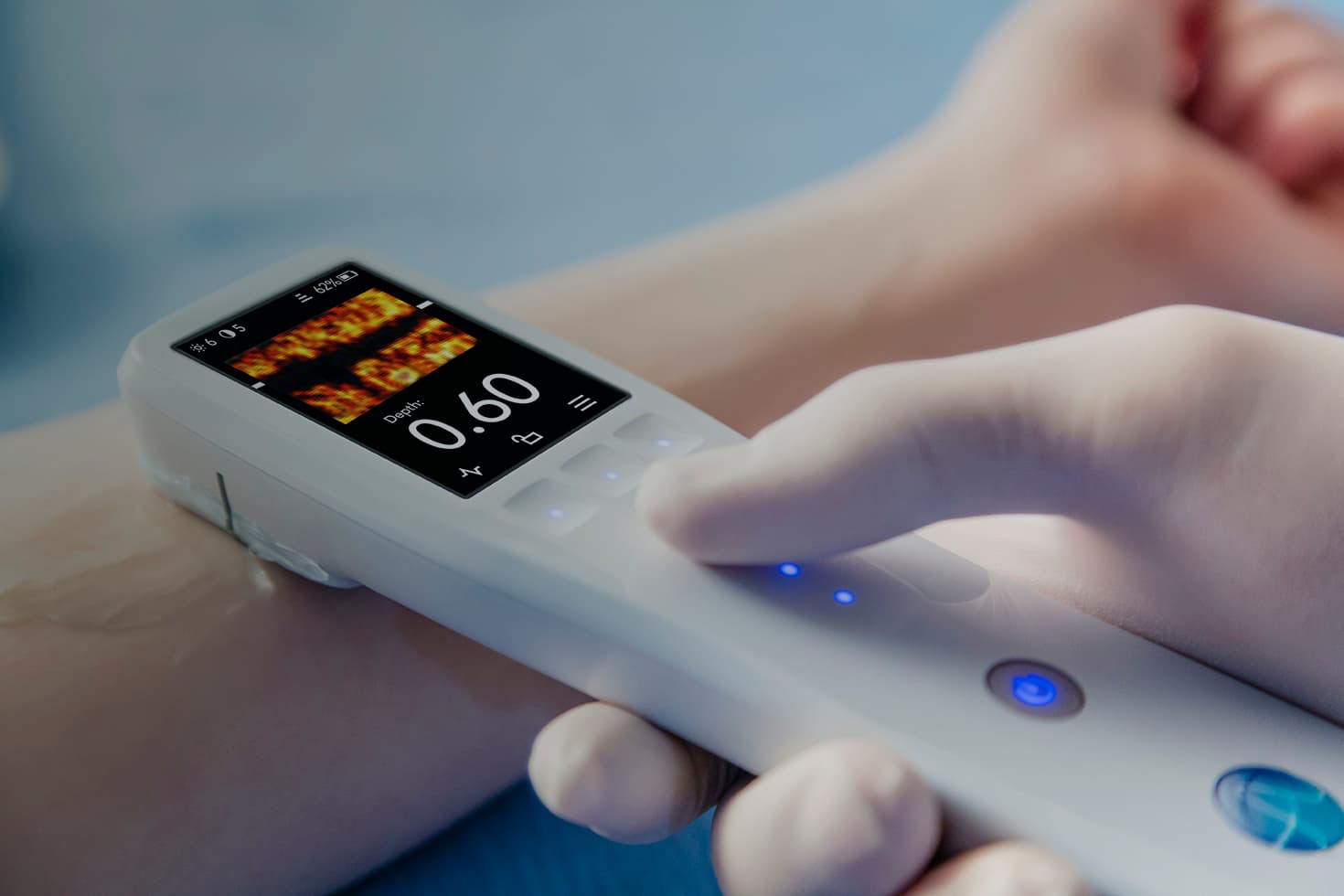
Delve is a medical device design consultancy that take your concepts to production through user research, strategy, design, and engineering expertise.
We assist from concept to launch of Class II and Class III medical devices. From creating user requirements and handling regulatory compliance, to developing medical device designs, selecting materials and supply chains, and assisting with FDA submissions.
Medical Device Development Expertise
Our Work
Baebies' sought our expertise in user research, industrial design, and shaping the user experience. We immersed ourselves in the NICU and turned Baebies' technology into a diagnostics device that's saving lives.
Winner
Winner
Winner
Winner
Your concept has already attracted backing, but to get to the next level you need design, technical expertise, and prototyping capacity. Our strategists, designers, and engineers have guided many startups to the next round. Or to an exit.
Medical Device Design Consultants
Medical device design consultants play a crucial role in developing and improving medical equipment. They combine their knowledge of engineering, medicine, and user experience to create efficient, safe, and user-friendly products. With the constant advancements in technology and the healthcare industry's growing needs, medical device design consulting has become an essential service for manufacturers. One significant aspect of this field is working with medical equipment design companies. These organizations specialize in developing innovative solutions to address complex challenges healthcare professionals face. By collaborating with skilled engineers and designers, they can identify problems and create devices that improve diagnostics, treatment, or patient care. This partnership between consultants and companies ensures that the final product meets the necessary regulatory standards while also meeting end-users' expectations.
Another critical service provided by these experts is a medical device design consultancy. This involves guiding clients through every step of the product development process – from concept generation to prototyping and testing. By offering their expertise on various aspects such as materials selection, ergonomics, usability, and manufacturing processes, consultants help clients make informed decisions about their designs. Additionally, they ensure compliance with relevant regulations such as FDA requirements or CE marking guidelines.
The role of medical device design consultants extends further into providing guidance on post-market surveillance programs and risk management strategies. This support helps businesses continuously monitor their products' performance in real-world settings and take corrective action if necessary. In recent years, there has been a growing demand for specialized medical device consulting companies that offer expert advice on various industry segments such as diagnostics, surgical instruments, or implantable devices.
These firms bring together a team of multidisciplinary professionals who understand technical aspects, market dynamics, and regulatory requirements specific to each segment. Overall, engaging with professional medical device design consultants offers numerous benefits for manufacturers aiming to develop innovative solutions that positively impact patient care while adhering to strict regulatory standards. By partnering with experienced professionals who possess a thorough knowledge of current technologies and industry trends, companies can navigate the complex process of creating cutting-edge medical equipment with confidence and success.
Medical Product Design
Medical product design is a critical aspect of the healthcare industry, as it involves the creation of innovative solutions and devices that cater to various medical needs. These designs focus on improving patient care, enhancing diagnostic accuracy, and optimizing treatment outcomes. A highly specialized team of professionals, including medical device design engineers, industrial designers for medical devices, and medical device developers, contribute their expertise to ensure that these products are safe, effective, and user-friendly.
A medical device design engineer plays a crucial role in developing new products. They are responsible for conceptualizing and creating prototype devices to address specific health concerns or improve existing treatments. This process often includes rigorous research on market demands and emerging technologies to develop cutting-edge solutions tailored to customer needs. The engineer's primary goal is to ensure that the final product meets all regulatory standards while ensuring optimum performance. Industrial design for medical devices is another essential ingredient in this field.
Industrial designers work hand-in-hand with engineers and other stakeholders to create visually appealing yet functional products that cater to different user groups. Their primary task is to ensure usability, ergonomics, and aesthetics are seamlessly integrated into each device. By focusing on these elements, industrial designers help create products that not only serve their intended purpose but also make a positive impact on patients' lives.
Developing a successful medical product requires a collaborative approach from numerous specialists in various disciplines. Among them is the medical device developer who oversees the entire process from concept generation through manufacturing and distribution. Their role encompasses project management responsibilities, budgeting decisions, risk assessment analysis, quality control measures implementation, and liaising with vendors and suppliers.
To round out this diverse group of experts is the medical device engineer, whose main responsibility revolves around ensuring design feasibility during each stage of development. They assess prototyping materials selection, suitability of fabrication methods, and validating functionality against predetermined specifications using simulation software models or physical testing setups when necessary.
Medical product design is a complex and collaborative process that brings together the skills and expertise of various professionals to create innovative solutions in healthcare. From medical device design engineers to industrial designers, medical device developers, and medical device engineers – each plays a pivotal role in transforming ideas into life-saving products. Their collective efforts ensure that every medical device meets the highest safety, effectiveness, and usability standards for patients worldwide.
Medical Device Prototyping Services
Medical device prototyping services are essential in developing innovative healthcare solutions. These services encompass various methodologies and techniques to create functional and aesthetically pleasing prototypes accurately representing the final product. The prototypes are valuable tools for testing, validating, and refining medical devices, ultimately ensuring their efficacy, safety, and compliance with regulatory standards. Furthermore, medical device prototyping enables engineers and designers to identify potential issues, optimize performance, and streamline manufacturing processes. Among the many facets of medical device engineering are class I, II, and III classifications, which differ in terms of risk levels associated with these devices. Each classification requires unique approaches to design, development, testing, and regulatory approval processes.
Class I medical device engineering focuses on low-risk devices with minimal potential patient harm. Examples include stethoscopes or tongue depressors that are generally non-invasive and do not require intricate design features or complex manufacturing procedures. Nevertheless, class I medical devices must still meet specific quality assurance standards and regulatory requirements to guarantee their safety when used by healthcare professionals.
On the other hand, class II medical device engineering addresses moderate-risk products such as infusion pumps or surgical drapes that involve more complex designs and manufacturing processes compared to class I devices. These types of devices necessitate specialized expertise from developers who are skilled in addressing a myriad of factors, including material selection and electrical compatibility concerns, among other aspects crucial to ensuring patient safety while maximizing functionality.
Lastly, class III medical device engineering involves high-risk products directly interacting with a patient's vital systems or sustaining life, including pacemakers or heart valves. The development of these life-critical devices demands stringent adherence to rigorous standards concerning design control procedures, clinical trials data documentation, and regulatory submissions throughout the entire development process.
Medical device prototyping services are critical in bringing innovative healthcare solutions into reality by facilitating the iterative refinement of designs through physical models and testing. The classification of medical devices as class I, II, or III significantly impacts the engineering approaches employed in development, with each class demanding unique expertise and regulatory compliance measures that ensure their safety, efficacy, and market success. By leveraging these prototyping services in conjunction with specialized knowledge of various device classifications, healthcare organizations can accelerate the development timeline while maintaining high-quality standards for their innovative medical solutions.
Medical Device Innovation
Medical device innovation has become a critical aspect of the healthcare industry, as it plays a vital role in improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs. The continuous advancements in technology have led to the development of state-of-the-art medical devices that can be classified into three categories: class I medical device innovation, class II medical device innovation, and class III medical device innovation. Each of these classifications is based on the risk of using a particular device and its intended application.
Class I medical device innovation mainly involves low-risk devices that are typically non-invasive or minimally invasive. These devices usually have a straightforward design and function, ensuring user safety and reliability. Examples of class I medical devices include stethoscopes, bandages, manual wheelchairs, and surgical instruments such as scalpels. This category's innovations enhance functionality, usability, and affordability while maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements.
As we delve further into the complexities of medical device innovation, class II medical devices come into play. These moderate-risk devices may require stringent controls to ensure their safety and efficacy. Class II devices comprise various products, such as infusion pumps, powered wheelchairs, X-ray machines, and blood glucose monitors. Innovations in this category aim to improve accuracy, efficiency, and patient comfort while still adhering to necessary regulatory standards.
Lastly, class III medical device innovation encompasses high-risk devices that support or sustain human life or prevent significant impairment to health if they fail to perform as expected. Such innovations often involve cutting-edge technology for novel therapeutic applications or sophisticated diagnostic procedures. Examples include implantable pacemakers, artificial heart valves, and neurostimulators for deep brain stimulation therapy in Parkinson's disease patients. These groundbreaking innovations necessitate rigorous clinical trials and strict regulatory oversight to ensure patient safety without compromising performance.
Medical device innovation spans various risk levels, encompassing class I through class III devices. Each device class demands distinct considerations regarding design, functionality, and regulatory compliance. The continuous evolution and growth of medical device innovation not only improve patient care but also contribute to the overall advancement of the healthcare industry. As research progresses and technologies advance, we can expect further enhancements in medical devices that cater to diverse applications and unique patient needs across all classes.